Looking for ways to trade crude oil futures or micro crude oil more effectively? Whether you’re a short-term trader who’s in and out of the market multiple times a day or a longer-term trader holding positions for days or weeks, there are several fundamental, economic, and technical analysis concepts related to trading crude oil futures that you need to recognize. Having a strong conceptual understanding of these fundamental factors can help you become a more complete trader and make better, more informed trading decisions and crude oil analysis.
- What factors can drive the price of crude oil futures?
- What is the historical seasonal pattern of crude oil futures?
- What are the intermarket relationships with crude oil futures?
- Who are the big traders in the crude oil futures market?
In this article, we’ll cover the fundamental analysis of crude oil futures and explore crude oil’s importance in global energy production, transportation fuels, and many industrial processes.
How Is Crude Oil Used Around the World?
Crude oil is a critical global resource that serves multiple purposes in our everyday lives. It can be refined into transportation fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. It’s also a fundamental component in creating plastics, pharmaceuticals, and many other products, making it an essential commodity traded widely in financial markets all over the world.
What Can Affect the Price of Crude Oil Futures?
Like most products and commodities, supply and demand dynamics are key fundamental factors that influence the price of crude oil. Changes in production levels (supply) by countries with oil reserves can affect how much crude oil is available on the market. The increasing or decreasing demand for energy, gasoline, and other crude oil byproducts can have both short- and long-term effects on crude oil prices.
For example, here in the US, an especially cold winter can drive up the demand and prices for heating oil. Likewise, strong economic growth can increase the energy needs for new construction, recreational activities, and other expanding business activities.
Both the International Energy Agency (IEA) and U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) focus on collecting, analyzing, and reporting data related to all areas of energy production. By tracking supply and demand metrics for most key energy resources, they can better help shape energy policy. You can track the supply and demand of crude oil in the US and around the world through the EIA and IEA.
Crude oil prices can also be sensitive to changes in the value of the U.S. dollar (USD), geopolitical news, and other economic factors.
USD
The USD plays a significant role in the pricing of crude oil as most international crude oil transactions are conducted in USD. This has created a strong correlation between the USD and the crude oil market. Crude oil is often priced in USD, with major benchmark products such as Brent (North Sea) and WTI (West Texas Intermediate) quoted in USD per barrel. This means that fluctuations in the value of the USD can often directly impact the price of crude oil.
Geopolitical and Geoeconomic Factors
Geopolitical and geoeconomic factors like international conflicts and political instability can lead to supply disruption, which can drive the price of crude oil higher. The energy policies of individual countries and other groups like the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) can also have a significant effect on the price of crude oil.
What is OPEC?
OPEC is a group of 12 oil-producing nations (Algeria, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, the Republic of the Congo, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Venezuela) that directs the daily production amount of crude oil within its group members. In 2021, OPEC members accounted for nearly 40% of all crude oil production globally.
There are other fundamental factors that can affect the price of crude oil over both the short and long term. Traders wanting to profit from price movements in the crude oil futures market should keep abreast of current economic news and events and have a good understanding of key fundamental pricing factors in the crude oil market. Here’s a weekly price chart showing the performance of crude oil futures. (Figure 1)

Figure 1: Blue line = Weekly crude oil price chart from 2018 to 2024 with 52-week simple moving average, showing the long-term price fluctuation of crude oil driven by market fundamentals, economic news, and geopolitical events.
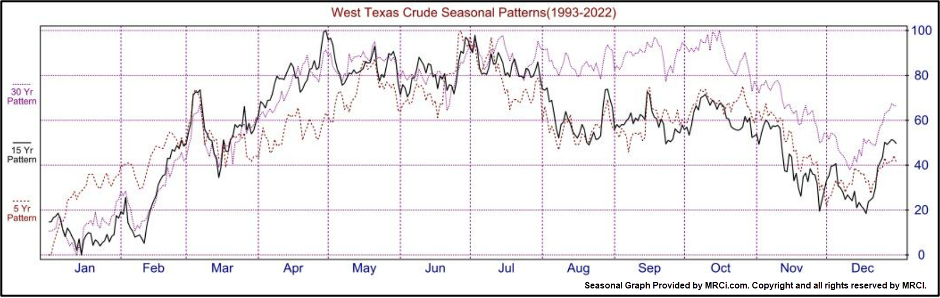
Seasonality Patterns of Crude Oil Futures
Seasonality is the analysis of historical price patterns throughout the year. The current crude oil seasonality 15-year pattern (black line) typically sees prices rise mid-December through April, with sideways price action until July, then lower prices through August, then sideways action again through October, with lower prices until mid-December. (Figure 2)
CFTC Commitment of Traders Report for Crude Oil Futures
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) requires all large traders to report their open futures positions every week, which the CFTC then publishes in the Commitment of Traders (COT) report. Below is the COT indicator for the crude oil futures available on the NinjaTrader platform, which shows the net position for each group of traders (Figure 3).
Typically, the commercial traders (in blue) are hedging the price of crude oil to better control costs and lock in prices for their business. Although these traders are typically net short, when commercial traders are getting more net short, prices tend to rise; when they are getting more net long, prices tend to fall.
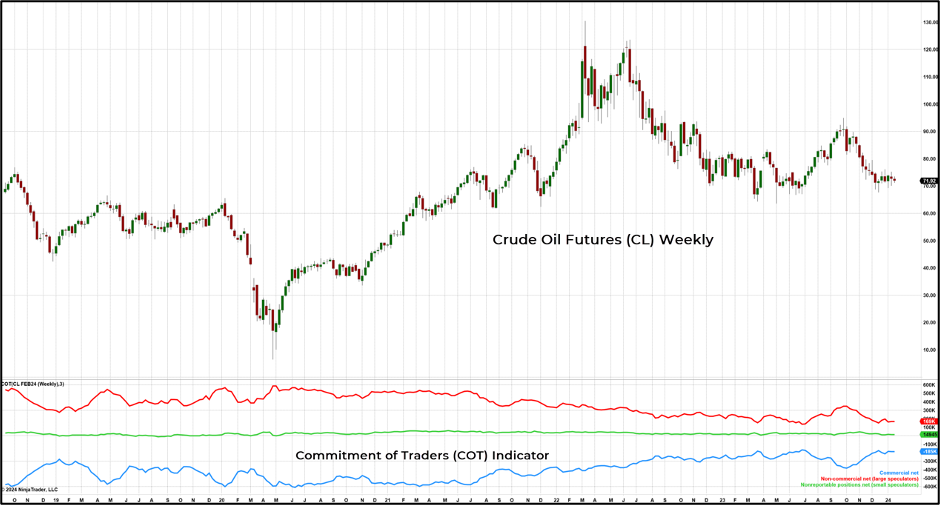
Figure 3: The COT net positions report for crude oil futures.
Red line = Net large speculators
Blue line = Net commercial traders
Green line = Net non-reporting positions
What Affects the Intraday Price of Crude Oil?
The intraday price of crude oil can fluctuate greatly based on traders’ sentiment and expectations. Daily price movements in crude oil often result from intermarket relationships, supply and demand dynamics, and economic news reports. Traders looking to speculate on the intraday price movement of crude oil will generally employ a variety of short- and long-term historical price charts, using a variety of technical analysis tools to gauge trend direction, support and resistance levels, and increasing or decreasing momentum.
Level Up Your Futures Trading With These Crude Oil Analysis Skills
We’ve covered many of the concepts of analyzing the fundamentals of the crude oil futures market. Every trader will have their own approach to market analysis, combining both fundamental and technical analysis into a trading plan to help make more consistent trading decisions.
Crude oil, like many futures markets, is often news-driven, meaning price action can act contrary to your analysis. It’s important to remember when key economic reports and news are going to be released and either avoid high-volatility environments altogether or protect your orders and positions with aggressive risk management. Determining when to get in and out of a crude oil position is only part of a comprehensive trading plan that includes trade sizing, risk management, and setting goals and objectives.
Unlock Free Exclusive Training
Explore the foundational concepts of fundamental and technical analysis with our free multi-video trading course “Technical Analysis Made Easy.” Learn how to analyze and anticipate market movements using market prices, volume data, and more. To access this and other exclusive on-demand courses and educational content, sign up for your free NinjaTrader account today.
And watch our daily livestream events as we prepare, analyze, and trade futures markets in real time.